1 广东大湾区空天信息研究院,广东 广州 510530
2 武汉国家光电研究中心,湖北 武汉 430074
3 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
4 俄罗斯研究中心库尔恰托夫研究所,俄罗斯莫斯科 125047
极紫外光源在半导体制造中的掩模检测、显微成像以及光谱计量等环节中有着重要的应用。激光诱导放电等离子体是产生极紫外光源的重要技术手段之一,搭建了一套二氧化碳激光诱导放电产生锡等离子体的实验装置,对产生的极紫外光谱进行了收集探测,并结合辐射磁流体动力学模拟对极紫外的辐射特性进行了分析。实验对比了激光等离子体和放电等离子体的极紫外辐射特性的区别,发现放电电压对激光诱导放电等离子体极紫外光的带内辐射强度有着重要影响。模拟发现,当电压为15 kV时,极紫外辐射总能量达到65.0 mJ,转化效率达到0.23%,光谱纯度达到1.69%。
激光光学 激光诱导放电等离子体 极紫外光 辐射磁流体动力学 转化效率
1 广东大湾区空天信息研究院,广东 广州 510700
2 广东省太赫兹量子电磁学重点实验室,广东 广州 510700
3 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
深紫外激光具有光子能量高、波长短等特点,在激光加工、半导体光刻等领域中具有重要的应用价值。固体激光非线性频率变换是实现高功率、高相干性深紫外激光输出的主要方式之一。采用全固态532 nm激光作为基频光、国产商用CsLiB6O10(CLBO)晶体作为频率变换晶体,在基频光功率为34.2 W时,实现了平均功率为14 W、重复频率为100 kHz、脉冲宽度为1.8 ns的266 nm深紫外激光输出,光-光转换效率达到41%。该深紫外光源具有效率高、结构紧凑的优点,验证了国产商用CLBO晶体的实用性,可进一步获得更稳定、更高功率的深紫外激光输出。
激光器 深紫外激光 全固态激光 CsLiB6O10晶体 高功率

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Chinese Academy of Sciences, GBA branch of Aerospace Information Research Institute, Guangzhou, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
A 60-mW solid-state deep ultraviolet (DUV) laser at 193 nm with narrow linewidth is obtained with two stages of sum frequency generation in LBO crystals. The pump lasers, at 258 and 1553 nm, are derived from a homemade Yb-hybrid laser employing fourth-harmonic generation and Er-doped fiber laser, respectively. The Yb-hybrid laser, finally, is power scaling by a 2 mm × 2 mm × 30 mm Yb:YAG bulk crystal. Accompanied by the generated 220-mW DUV laser at 221 nm, the 193-nm laser delivers an average power of 60 mW with a pulse duration of 4.6 ns, a repetition rate of 6 kHz, and a linewidth of ∼640 MHz. To the best of our knowledge, this is the highest power of 193- and 221-nm laser generated by an LBO crystal ever reported as well as the narrowest linewidth of 193-nm laser by it. Remarkably, the conversion efficiency reaches 27% for 221 to 193 nm and 3% for 258 to 193 nm, which are the highest efficiency values reported to date. We demonstrate the huge potential of LBO crystals for producing hundreds of milliwatt or even watt level 193-nm laser, which also paves a brand-new way to generate other DUV laser wavelengths.
193 nm solid-state laser deep ultraviolet LBO crystal sum frequency mixing narrow linewidth Advanced Photonics Nexus
2024, 3(2): 026012
1 山东大学信息科学与工程学院, 山东省激光技术与应用重点实验室, 山东 青岛 266237
2 山东大学激光与红外系统集成技术教育部重点实验室, 山东 青岛 266237
3 广东大湾区空天信息研究院, 广东 广州 510700
4 东京大学物性研究所, 日本 千叶 277-8581
综述了真空紫外193 nm波段固体激光光源的发展情况,具体包括所涉及到的主要非线性晶体[偏硼酸钡(BBO)晶体、三硼酸锂(LBO)晶体、六硼酸铯锂(CLBO)晶体、氟代硼铍酸钾(KBBF)晶体等]的各类特性及其对比分析、近几十年来193 nm波段连续固体激光和脉冲固体激光的发展脉络、用于产生193 nm固体激光的各种基频光源组合,并对它们的优劣势进行了分类分析和对比。对影响非线性晶体紫外透过率和紫外激光输出功率的双光子吸收效应进行了描述,并对深紫外激光器中的激光诱导污染效应进行了描述,指出几类常用的避免或者缓解该效应的方法。最后对实现超高重复频率准连续真空紫外激光的难度和应当解决的问题进行了探讨。
光学学报
2022, 42(11): 1134010
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shaanxi Joint Laboratory of Graphene, State Key Laboratory of Photoelectric Technology and Functional Materials, International Collaborative Center on Photoelectric Technology and Nano Functional Materials, Institute of Photonics & Photon-Technology, School of Physics, Northwest University, Xi’an 710069, China
2 School of Science, Xi’an University of Posts and Telecommunications, Xi’an 710121, China
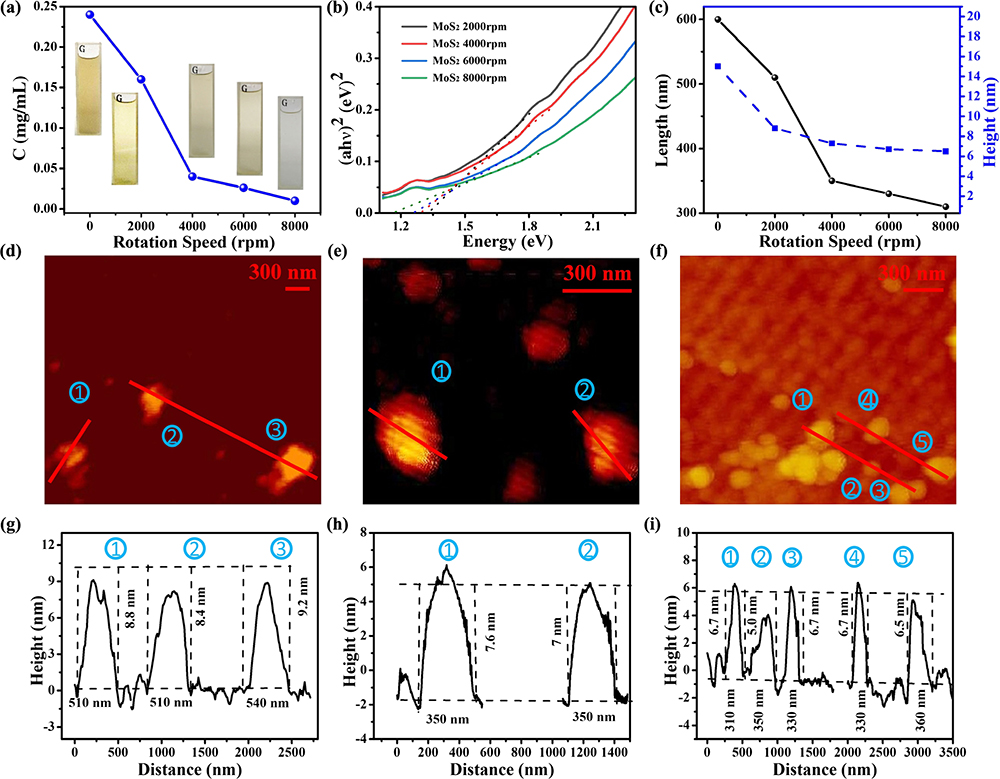
Understanding and controlling defect in two-dimensional materials is important for both linear and nonlinear optoelectronic devices, especially in terms of tuning nonlinear optical absorption. Taking advantage of an atomic defect formed easily by smaller size, molybdenum disulfide nanosheet is prepared successfully with a different size by gradient centrifugation. Interestingly, size-dependent sulfur vacancies are observed by high-resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. The defect effect on nonlinear absorption is investigated by Z-scan measurement at the wavelength of 800 nm. The results suggest the transition from saturable absorption to reverse saturable absorption can be observed in both dispersions and films. First principle calculations suggest that sulfur vacancies act as the trap state to capture the excited electrons. Moreover, an energy-level model with the trap state is put forward to explain the role of the sulfur vacancy defect in nonlinear optical absorption. The results suggest that saturable absorption and reverse saturable absorption originate from the competition between the excited, defect state and ground state absorption. Our finding provides a way to tune the nonlinear optical performance of optoelectronic devices by defect engineering.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(9): 09001512





